How Technology is Transforming Orthopaedic Surgery in 2026
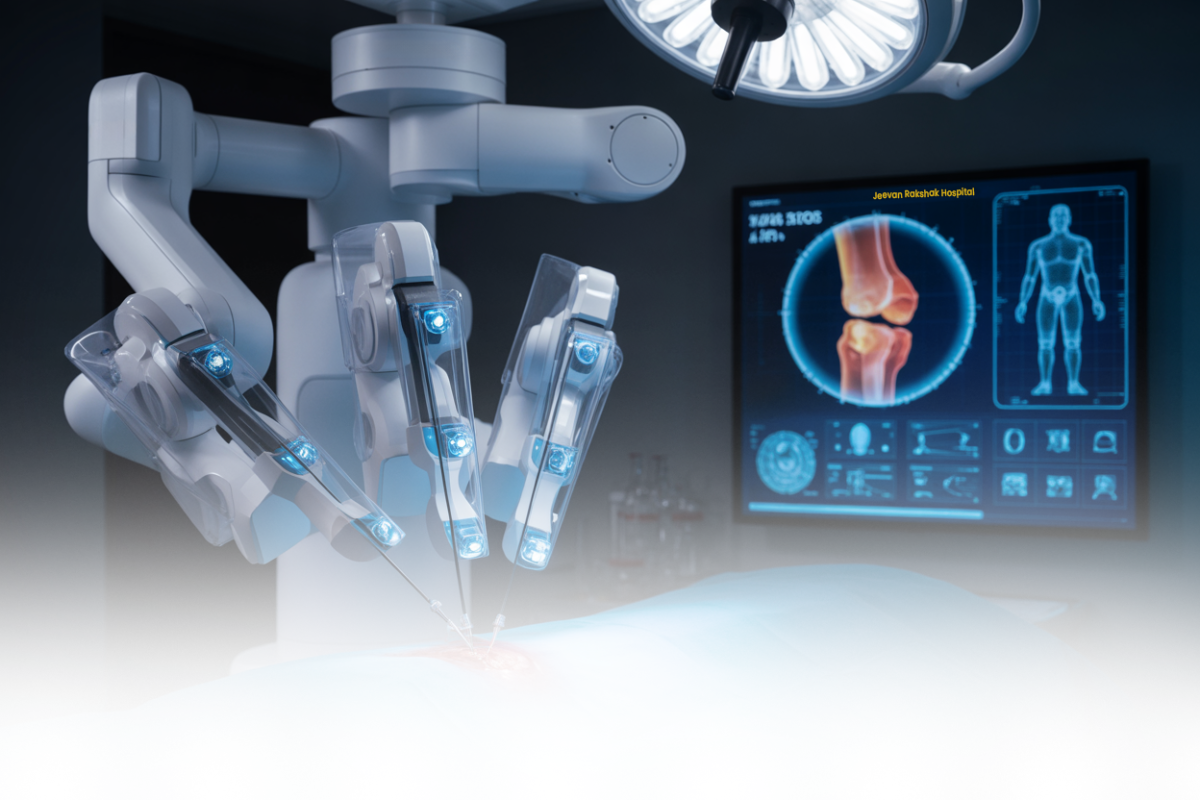
Orthopaedic surgery is experiencing its most significant transformation in decades. In 2026, cutting-edge technologies are revolutionizing how surgeons diagnose conditions, plan procedures, execute operations, and monitor patient recovery. From artificial intelligence to robotic systems and smart implants, these innovations are delivering unprecedented precision, faster recoveries, and better long-term outcomes for patients worldwide.
The Digital Revolution in Orthopaedics
The convergence of artificial intelligence, robotics, and advanced imaging has created what many experts call the “digital orthopaedic revolution.” These technologies aren’t just supplementing traditional techniques—they’re fundamentally reshaping surgical workflows and enabling procedures that were previously impossible or too risky.
Modern orthopaedic surgeons now have access to tools that can analyze thousands of surgical cases in seconds, create patient-specific surgical plans, and execute procedures with submillimeter accuracy. This technological leap is democratizing surgical excellence, allowing surgeons of all experience levels to achieve outcomes previously reserved for only the most skilled specialists.
Artificial Intelligence: The Game-Changing Assistant
Rapid Surgical Planning
AI has dramatically accelerated preoperative planning. What once took weeks of manual calculations and measurements now happens in minutes. AI algorithms analyze CT and MRI scans to create detailed 3D anatomical models, recommend optimal implant sizes and positions, and predict potential complications before surgery begins.
Surgeons report that AI-generated surgical plans achieve 98% accuracy in fracture detection and tumor identification. This precision translates directly to better patient outcomes and fewer revision surgeries.
Intraoperative Decision Support
During surgery, AI provides real-time guidance by analyzing live imaging data and adjusting recommendations based on actual tissue conditions. Advanced systems like X23D can create 3D spinal models from just four fluoroscopy images, enabling precise pedicle screw placement while reducing radiation exposure by 70%.
Predictive Analytics
AI algorithms can now predict patient recovery trajectories, identify those at high risk for complications, and recommend personalized rehabilitation protocols. This proactive approach allows early intervention when problems arise, significantly improving recovery outcomes.
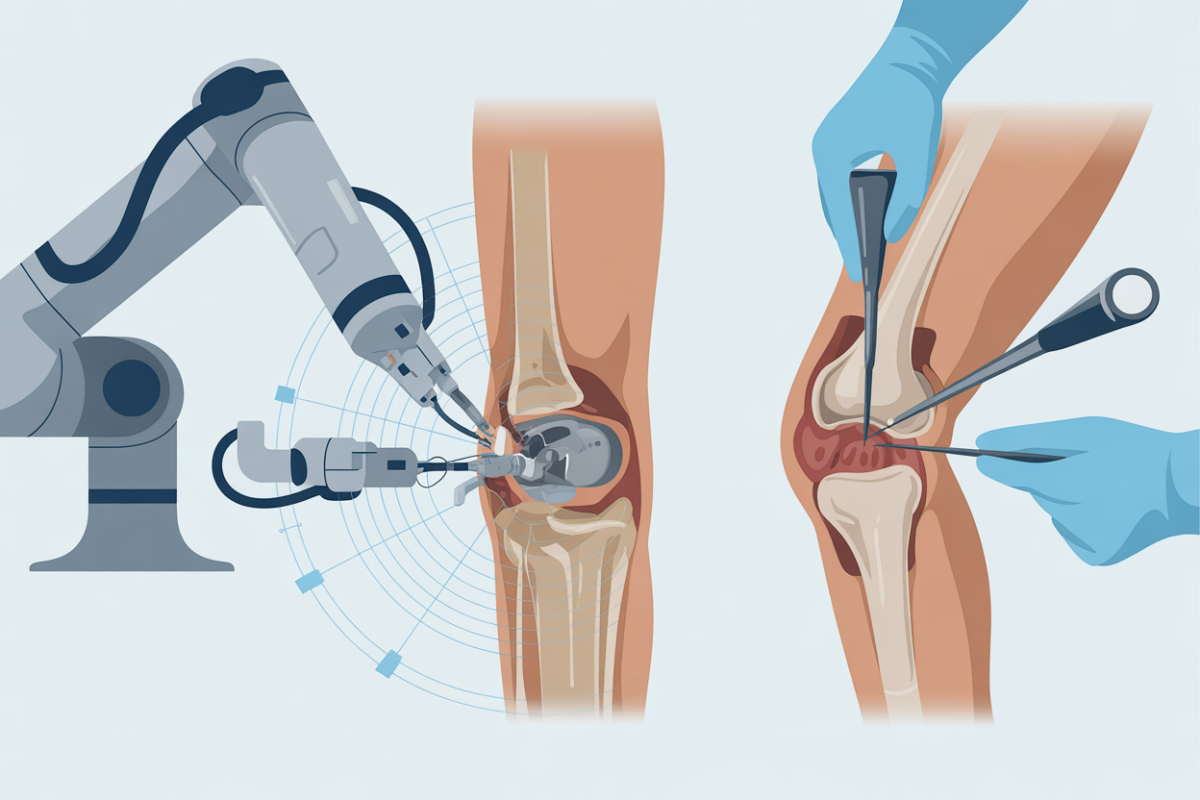
Robotic Surgery: Precision Beyond Human Capability
Advanced Hip and Knee Replacements
Robotic-assisted joint replacement has matured significantly in 2026. Current systems achieve 99.9% implant alignment accuracy compared to 69.9% with traditional methods. This dramatic improvement means implants last longer, function better, and require fewer revisions.
By 2030, experts predict two out of every three total hip arthroplasties will be performed robotically, along with one in two total knee replacements. The technology has proven particularly valuable for complex cases involving unusual anatomy or significant deformities.
Expanding to Shoulder Surgery
A major breakthrough in 2026 is the commercial availability of robotic systems specifically designed for total shoulder arthroplasty. These systems help surgeons achieve superior outcomes that are reproducible across all skill levels, addressing the high revision rates historically seen in shoulder replacements due to incorrect prosthesis placement.
Faster, More Efficient Procedures
Robotic systems like TiRobot reduce operative time by 20% through automated instrument positioning and real-time optical tracking. This efficiency reduces anesthesia exposure, lowers infection risk, and allows surgical centers to serve more patients without compromising quality.
Augmented Reality: Seeing Through the Body
3D Visualization During Surgery
Augmented reality (AR) technology has moved from experimental to essential in 2026. Systems like Philips’ ClarifEye combine intraoperative CT scans with AR navigation, superimposing high-resolution 3D anatomical models directly onto the surgical field in real-time.
This technology eliminates guesswork by allowing surgeons to “see through” tissues and visualize critical structures like blood vessels and nerves before making incisions. The result is greater precision and fewer complications.
Smart Glasses in the Operating Room
Wearable smart glasses are revolutionizing how surgeons interact with imaging data during procedures. Instead of turning away from the surgical field to view monitors, surgeons can see critical information displayed directly in their field of vision, maintaining focus and improving efficiency.
Smart Implants and Digital Twins
Real-Time Recovery Monitoring
Smart implants equipped with sensors provide continuous data on healing progress, weight distribution, and implant stability. This real-time feedback allows surgeons to detect problems early—often before patients experience symptoms—and adjust rehabilitation protocols accordingly.
Personalized Digital Replicas
Digital twin technology creates virtual replicas of individual patients’ anatomy and physiology. Surgeons can test multiple treatment approaches on these digital models before actual implementation, predicting outcomes with remarkable accuracy and choosing the optimal strategy for each patient.
3D Printing: Customization at Scale
Patient-Specific Implants
Advanced 3D printing technology enables the creation of implants customized to each patient’s unique anatomy. These patient-specific devices fit better, function more naturally, and often last longer than standard off-the-shelf alternatives.
The integration of AI with 3D printing allows for rapid design and production of custom surgical guides, implants, and bone grafts tailored to individual cases.
Preoperative Practice Models
Surgeons can now 3D-print exact replicas of patients’ bones and joints to practice complex procedures before entering the operating room. This rehearsal capability is particularly valuable for challenging cases involving fractures, deformities, or revision surgeries.
Minimally Invasive Advancements
Smaller Incisions, Better Outcomes
Technology has enabled dramatically less invasive approaches to orthopaedic procedures. Robotic precision allows surgeons to work through smaller incisions while maintaining or improving surgical accuracy, resulting in:
Less tissue damage and bleeding
Reduced post-operative pain
Faster recovery and return to activity
Smaller, less visible scars
Lower infection rates
Outpatient Joint Replacement
Thanks to technological advances and improved pain management protocols, many procedures that once required multi-day hospital stays can now be performed in outpatient ambulatory surgery centers. Same-day total joint replacements are becoming routine, offering convenience to patients and reducing healthcare costs.
Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy
AI-Powered Image Analysis
Artificial intelligence has transformed diagnostic imaging in orthopaedics. AI algorithms can analyze X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans with accuracy matching or exceeding human radiologists, detecting subtle fractures, early arthritis, tumors, and implant complications that might be missed by the human eye.
This enhanced detection capability leads to earlier diagnosis and treatment, often preventing conditions from progressing to stages requiring surgery.
Automated Implant Identification
AI systems can now automatically identify and classify orthopaedic implants from imaging studies. This capability is invaluable for patients who need revision surgery but lack records of their original implant type, saving time and reducing surgical complications.
The Benefits for Patients
Shorter Recovery Times
The combination of minimally invasive techniques, precise surgical execution, and AI-optimized rehabilitation protocols has reduced recovery times by up to 20%. Patients return to work, sports, and daily activities faster than ever before.
Better Long-Term Outcomes
Improved surgical precision translates directly to better long-term function. Properly aligned implants experience less wear, reducing the likelihood of revision surgery and extending implant lifespan well beyond 20 years in many cases.
Personalized Care Pathways
Technology enables truly individualized treatment plans based on each patient’s specific anatomy, activity level, bone quality, and health status. This personalization ensures patients receive exactly the care they need, not one-size-fits-all protocols.
Reduced Complications
AI-guided surgery, robotic precision, and real-time monitoring combine to significantly reduce complication rates. Studies show robotic procedures reduce major complications by 50-70%, with infection rates below 0.5%.
Challenges and Considerations
The Learning Curve
While technology enhances surgical capability, it requires training and adaptation. Surgeons must invest time learning new systems, and there’s an initial learning curve that can temporarily extend operative times.
Cost Considerations
Advanced robotic and AI systems represent significant upfront investments for hospitals and surgical centers. However, many facilities find that improved outcomes, higher efficiency, and reduced revision rates offset these initial costs over time.
Technology Access
Not all patients have equal access to these advanced technologies. Geographic location, insurance coverage, and facility resources can create disparities in who benefits from the latest innovations.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Orthopaedic Surgery
Autonomous Surgical Systems
While current robotic systems require constant surgeon control, research is advancing toward semi-autonomous systems that can execute routine portions of procedures under surgeon supervision. These developments could further improve consistency and reduce surgeon fatigue during lengthy operations.
Integration with Wearable Technology
Smart implants will increasingly integrate with wearable fitness trackers and health monitors, creating comprehensive pictures of patient activity, recovery progress, and implant performance over years or decades.
Continued Miniaturization
As mechanics become smaller and more precise, surgical techniques will become even less invasive. Procedures that currently require several small incisions may eventually be performed through single tiny ports.
What This Means for You
If you’re considering orthopaedic surgery in 2026, these technological advances offer significant advantages:
Ask about robotic assistance – Inquire whether your surgeon uses robotic or navigation systems for your procedure
Explore AI planning – Request information about AI-assisted surgical planning and how it might benefit your case
Discuss outpatient options – Many procedures can now be done on an outpatient basis with proper planning
Understand your implant – Ask whether patient-specific or smart implants are options for your situation
Consider surgeon experience – Choose surgeons who have embraced new technologies and received proper training
The Bottom Line
Technology is fundamentally transforming orthopaedic surgery in 2026, delivering benefits that seemed like science fiction just a decade ago. From AI that plans surgeries in minutes to robots that achieve submillimeter precision, from smart implants that monitor healing to AR systems that let surgeons see through tissue—these innovations are making procedures safer, more precise, and more personalized than ever before.
While technology is powerful, it remains a tool that enhances—not replaces—surgical expertise. The best outcomes come from the combination of cutting-edge technology in the hands of experienced, skilled surgeons who understand both the capabilities and limitations of these systems.
As these technologies continue to evolve and become more widely available, patients across India and around the world will benefit from the precision, safety, and improved outcomes they enable. The future of orthopaedic surgery isn’t coming—it’s already here.